Quality of Service (QoS) in Fiber Optic Networks

Quality of Service (QoS) is a critical network mechanism used to manage the quality of data traffic transmission and determine its priority on fiber optic networks. It ensures that various types of data traffic—such as voice, video, and standard data—receive the appropriate service levels. The key objectives of QoS include enabling networks and organizations to prioritize traffic, providing dedicated bandwidth, controlling jitter, and reducing latency. This capability is essential for enhancing the performance of business applications, Wide Area Networks (WANs), and service provider networks.
QoS networking technology operates by marking packets to identify their service types and configuring routers to create separate virtual queues for each application based on priority. As packets enter the system through the ingress interface, they are classified and marked. During this process, policing mechanisms may discard some packets. Once marked, packets undergo a second classification based on their identifiers. Congestion management and avoidance mechanisms then assign different priorities to various types of packets, ensuring that those with higher priority pass through gateways more quickly during network congestion. Finally, the processed packets are transmitted through the egress interface using the QoS mechanism.
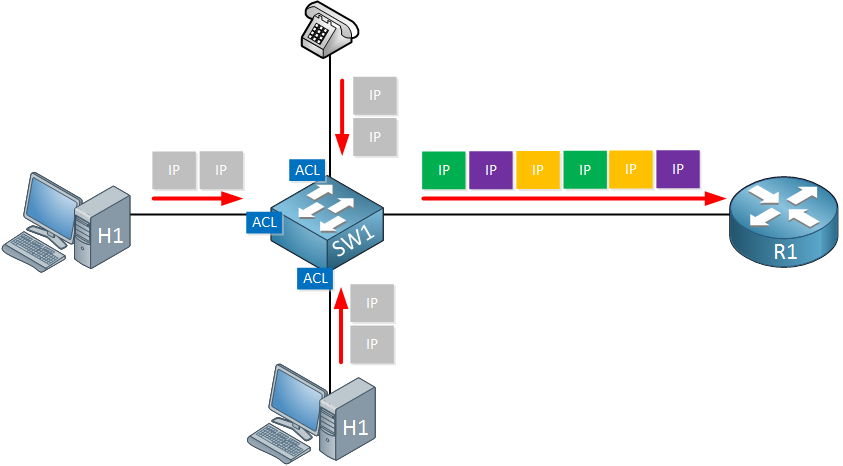
In an enterprise office setting, the need for QoS is evident. Beyond basic web browsing and email services, applications such as Telnet-based device login, remote video conferencing, real-time voice calls, FTP file transfers, and video playback require guaranteed network quality, especially during peak usage hours. If these services have varying quality requirements, corresponding QoS functions can be configured or enabled only for specific services.
Different applications have distinct QoS requirements. For instance, network protocols and management protocols like OSPF and Telnet necessitate low latency and a low packet loss rate without demanding high bandwidth. Through QoS’s priority mapping feature, packets from these applications can be marked with a higher service level, allowing network devices to prioritize their forwarding.
Real-time applications, including video conferencing and VoIP, have stringent demands for high bandwidth, low latency, and minimal jitter. QoS’s traffic shaping feature can be utilized to allocate sufficient bandwidth for video packets while increasing their priority to ensure seamless communication. VoIP services require low packet loss, low latency, and minimal jitter; thus, voice packet priorities are adjusted to be higher than those of video packets, ensuring they receive priority passage during congestion.

High data volume services, such as FTP transfers and database backups, involve extensive data transmission. These services require the lowest possible packet loss rate. Traffic shaping is configured for these packets to utilize data buffers, reducing packet loss caused by sudden traffic bursts.
For streaming media, like online audio streaming and video on demand, the requirements are less stringent since these programs are often pre-produced. Viewers can cache content, which minimizes the need for low latency, packet loss, and jitter. However, QoS’s priority mapping function can still be used to enhance the performance of these services when necessary.
Regular services, such as HTML web browsing and email, do not have specific network requirements and can operate under default settings without additional QoS features.
Historically, traditional business networks operated telephones and conference calls on one network while connecting laptops, desktops, and servers on another. This limited interaction and speed was not a priority when only data was being transmitted. Today, interactive applications that carry audio and video content demand high-speed transmission with no packet loss or speed variations. For organizations aiming to optimize performance for critical applications, implementing QoS is essential.
QoS guarantees that mission-critical applications will always have priority and the necessary resources for high performance. It allows administrators to better manage internet resources, effectively reducing costs and investment needs for link expansion. The ultimate goal of QoS is to ensure optimal performance for critical applications, enhancing user experience and productivity.